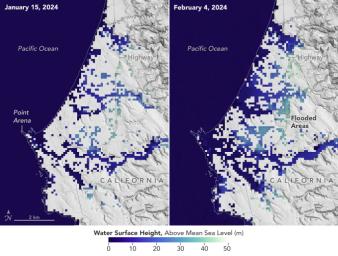
A series of atmospheric rivers drenched California in February 2024, with record amounts of rainfall and hurricane-force winds sweeping across parts of the state. The Surface Water and Ocean Topography (SWOT) mission captured data on coastal flooding near the community of Manchester, roughly 105 miles (169 kilometers) north of San Francisco. The satellite is a collaboration between NASA and the French space agency, CNES (Centre National d'Études Spatiales).
The image shows the area on Jan. 15, 2024, before the rain and snow from atmospheric rivers hit California, and then again on Feb. 4, 2024, after the first in a series of storms soaked the state. Water heights are shown in shades of green and blue, with lighter hues indicating the highest levels relative to mean sea level. (Data for inland areas includes the height of the floodwaters plus the ground elevation beneath it.) Each pixel in the image represents an area that is 330 feet by 330 feet (100 meters by 100 meters).
Since December 2022, SWOT has been measuring the height of nearly all water on Earth's surface, developing one of the most detailed, comprehensive views yet of the planet's oceans and freshwater lakes and rivers. Not only can the satellite detect the extent of the water on Earth's surface, as other satellites can, but SWOT can also provide water level data.
The mission science team made the measurements using the Ka-band Radar Interferometer (KaRIn) instrument. With two antennas spread 33 feet (10 meters) apart on a boom, KaRIn produces a pair of data swaths as it circles the globe, bouncing radar pulses off water surfaces to collect surface-height measurements.
Launched from Vandenberg Space Force Base in central California, SWOT is now in its operations phase, collecting data that will be used for research and other purposes.
SWOT was jointly developed by NASA and CNES, with contributions from the Canadian Space Agency (CSA) and the UK Space Agency. NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory, which is managed for the agency by Caltech in Pasadena, California, leads the U.S. component of the project. For the flight system payload, NASA provided the KaRIn instrument, a GPS science receiver, a laser retroreflector, a two-beam microwave radiometer, and NASA instrument operations. CNES provided the Doppler Orbitography and Radioposition Integrated by Satellite (DORIS) system, the dual frequency Poseidon altimeter (developed by Thales Alenia Space), the KaRIn radio-frequency subsystem (together with Thales Alenia Space and with support from the UK Space Agency), the satellite platform, and ground operations. CSA provided the KaRIn high-power transmitter assembly. NASA provided the launch vehicle and the agency's Launch Services Program, based at Kennedy Space Center, managed the associated launch services.
To learn more about SWOT, visit: https://swot.jpl.nasa.gov/

 Planetary Data System
Planetary Data System