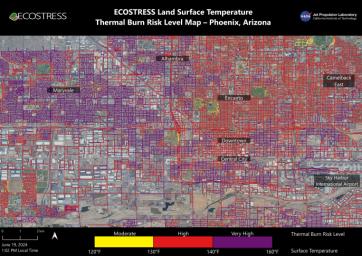
Data from NASA's ECOSTRESS (Ecosystem Spaceborne Thermal Radiometer Experiment on Space Station) instrument was used to map scorching pavement in Phoenix where contact with skin can cause serious burns. Based on measurements captured at 1:02 p.m. local time on June 19, 2024, the image shows land surface temperatures across a grid of roads and adjacent sidewalks, revealing how urban spaces can turn hazardous during hot weather.
The Arizona city's miles of asphalt and concrete surfaces (colored here in yellow, red, and purple, based on temperature) trap heat, as the image indicates. The surfaces registered at least 120 degrees Fahrenheit (49 degrees Celsius) to the touch – hot enough to cause contact burns in minutes to seconds.
At the lower right of the image is Phoenix Sky Harbor International Airport, where ECOSTRESS recorded some of the hottest land surface temperatures within the city – around 140 F (60 C). The air temperature on June 19 at the airport reached 106 F (43 C).
Air temperature, which is measured out of direct sunlight, can differ significantly from the temperature at the land surface. Streets are often the hottest surfaces of the built environment due to dark asphalt paving that absorbs more sunlight than lighter-colored surfaces; asphalt absorbs up to 95% of solar radiation. These types of surfaces can easily be 40 to 60 degrees F (22 to 33 degrees C) hotter than the air temperature on a very hot day.
Launched to the International Space Station in 2018, ECOSTRESS measures temperatures at the highest spatial resolution of any space-based instrument, producing images with a typical pixel size of about 225 feet (70 meters) by 125 feet (38 meters). The image of Phoenix was produced at higher spatial resolution using a machine learning algorithm that incorporates data from additional satellites: NASA/USGS Landsat and Sentinel-2. The combined measurements were used to "sharpen" the surface temperatures to a resolution of 100 feet (30 meters) by 100 feet (30 meters).

 Planetary Data System
Planetary Data System