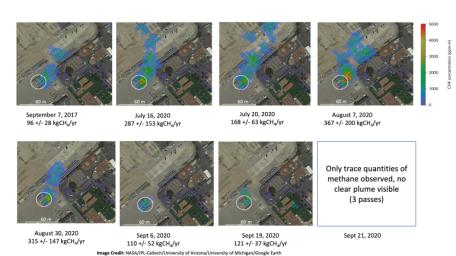
Figure 1Atmospheric methane is a potent greenhouse gas and an important contributor to air quality. Future instruments on orbiting satellites can help improve our understanding of important methane emission sources. NASA conducts periodic methane studies using the next-generation Airborne Visible/Infrared Imaging Spectrometer (AVIRIS-NG) instrument. These studies are determining the locations and magnitudes of the largest methane emission sources across California, including those associated with landfills, refineries, dairies, wastewater treatment plants, oil and gas fields, power plants, and natural gas infrastructure.
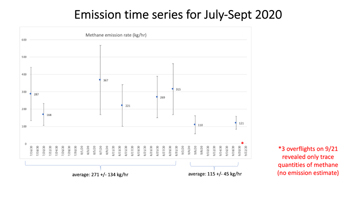
These images show concentrations of methane in a natural gas plume relative to background air measured by AVIRIS-NG, overlaid on true-color land surface images (source: Google Earth). The aircraft was flying at an altitude of about 10,000 feet (3,000 meters) above ground level and the AVIRIS-NG image pixels are each about 10 feet (3 meters) across. The plume shape varies with changing emission rate, wind speed and direction. The methane plume originates from a compressor — circled in each image — at Valley Generating Station, a natural gas-fired power plant near Los Angeles. The color scale indicates the concentration of methane in each pixel relative to background methane concentrations in the surrounding atmosphere. The plume was initially detected by a single overflight in September 2017 with an estimated methane emission rate of 96 +/- 28 kilograms/hour but assumed at the time to be due to normal operations (intermittent venting). The plume was detected by AVIRIS-NG again on six flights in July-August 2020 with a higher average emission rate for that period of 271 +/- 134 kgCH4/hr. AVIRIS-NG conducted multiple additional overflights on Sept 6, Sept 19, and Sept 21, 2020 and measured an average emission rate of 115 +/- 45 kgCH4/hr followed by 3 overflights on Sept 21, 2020 where only trace amounts of methane were detected.
For more information on AVIRIS-NG, visit https://avirisng.jpl.nasa.gov/.

 Planetary Data System
Planetary Data System