
Figure 1
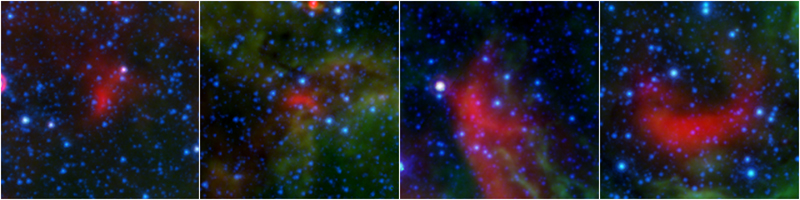
Figure 2

Figure 3
Click on images for larger versionsClick here for animation
This infrared image from NASA's Spitzer Space Telescope shows a cloud of gas and dust full of bubbles, which are inflated by wind and radiation from massive young stars. Each bubble is filled with hundreds to thousands of stars, which form from dense clouds of gas and dust.
The bubbles are estimated to be 10 to 30 light-years across, based on what astronomers know about them and other cosmic bubbles. However, determining the exact sizes of individual bubbles can be difficult, because their distance from Earth is challenging to measure and objects appear smaller the farther away they are.
Flows of particles called stellar winds emitted by the stars, as well as the pressure of the light those winds produce, can push the surrounding material outward, sometimes creating a distinct perimeter.
In Figure 1, the yellow circles and ovals outline more than 30 bubbles.
This active region of star formation is located inside the Milky Way galaxy, in the constellation Aquila (also known as the Eagle). Black veins running throughout the cloud are regions of especially dense cold dust and gas where even more new stars are likely to form.
The colors in this image represent different wavelengths of infrared light. Blue represents a wavelength of light primarily emitted by stars; dust and organic molecules called hydrocarbons appear green, and warm dust that's been heated by stars appears red.
Also visible are four bow shocks — red arcs of warm dust formed as winds from fast-moving stars push aside dust grains scattered sparsely through most of the nebula. The locations of the bow shocks are indicated by squares in Figure 1. Figure 2 shows zoomed-in views of the four bow shocks.
The bubbles and bow shocks in this image were identified as part of The Milky Way Project, a citizen science initiative on Zooniverse.org that seeks to map star formation throughout the galaxy. Participating citizen scientists looked through images from Spitzer's public data archive and identified as many bubbles as they could. More than 78,000 unique user accounts contributed. Astronomers running this program recently published a catalog of the bubble candidates that multiple citizen scientists had identified. The full Milky Way Project catalogs, which list a total of 2,600 bubbles and 599 bow shocks, are described in a paper published recently in Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society.
NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Pasadena, California, manages the Spitzer Space Telescope mission for NASA's Science Mission Directorate, Washington. Science operations are conducted at the Spitzer Science Center at Caltech in Pasadena, California. Spacecraft operations are based at Lockheed Martin Space Systems Company, Littleton, Colorado. Data are archived at the Infrared Science Archive housed at the Infrared Processing and Analysis Center (IPAC) at Caltech. Caltech manages JPL for NASA.
For more information about the Spitzer mission, visit http://www.nasa.gov/spitzer and http://spitzer.caltech.edu.

