Map Projected Browse Image
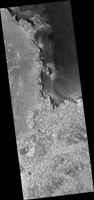
Click on the image for larger versionThis image from NASA's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter is reminiscent of the rugged and open terrain of a stark shore-line, perhaps of an island nation, such as the British Isles. A close-up in enhanced color produces a striking effect, giving the impression of a cloud-covered cliff edge with foamy waves crashing against it.
The reality is that the surface of Mars is much dryer than our imaginations might want to suggest. This is only a tiny part of a much larger structure; an inverted crater -- a crater that has been infilled by material that is more resistant to erosion than the rocks around it -- surrounded by bluish basaltic dunes. The edge of these elevated light-toned deposits are degraded, irregular and cliff-forming.
Dunes visible below the cliff, give the impression of an ocean surface, complete with foam capped waves crashing against the "shore line," demonstrating the abstract similarity between the nature of a turbulent ocean and a Martian dune field.
Meridiani Planum has an overall smooth terrain, which starkly contrasts with the more common boulder- and crater-laden landscapes observed over much of the rest of Mars. This makes it relatively younger in character than many other areas of the planet. Meridiani is one of the Mars Exploration Rover landing sites, and, is known for its layers and sediments. The orbital detection of hematite was one of the main reasons for sending Opportunity to this area.
Salt-bearing rocks -- also called sulphates -- were observed in the very first image from Opportunity, so perhaps it's apt that this HiRISE image reminds us of the turmoil and rugged beauty of a cliff-face, a coastline, being worn down by a relentless sea.
The map is projected here at a scale of 50 centimeters (19.7 inches) per pixel. [The original image scale is 54.7 centimeters (21.5 inches) per pixel (with 2 x 2 binning); objects on the order of 164 centimeters (64.6 inches) across are resolved.] North is up.
The University of Arizona, Tucson, operates HiRISE, which was built by Ball Aerospace & Technologies Corp., Boulder, Colo. NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory, a division of Caltech in Pasadena, California, manages the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter Project for NASA's Science Mission Directorate, Washington.

 Planetary Data System
Planetary Data System













