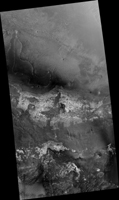
Map Projected Browse Image
Click on the image for larger versionSedimentary deposits are common within Valles Marineris. Most of the larger chasmata contain kilometer-thick light-toned layered deposits composed of sulfates. However, some of the chasmata, like Ius Chasma shown in this HiRISE image, either lack these deposits or have much thinner deposits.
The light-toned deposits in Ius Chasma are observed both along the floor and inner wallrock materials. Some of the light-toned deposits appear to post-date formation of the chasma floor, whereas other deposits appear to lie beneath wallrock materials, indicating they are older. By examining the stratigraphy using digital terrain models and 3D images, it should be possible to decipher the relative ages of the different geologic units. CRISM data may also provide insight into the mineralogy, which will tell scientists about the aqueous conditions that emplaced the light-toned deposits.
The University of Arizona, Tucson, operates HiRISE, which was built by Ball Aerospace & Technologies Corp., Boulder, Colorado. NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory, a division of the California Institute of Technology in Pasadena, manages the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter Project for NASA's Science Mission Directorate, Washington.

