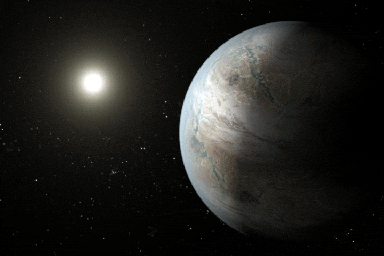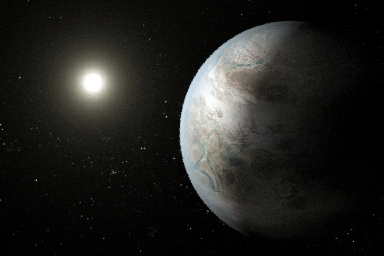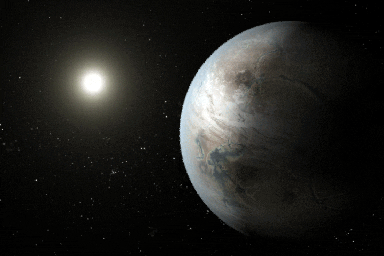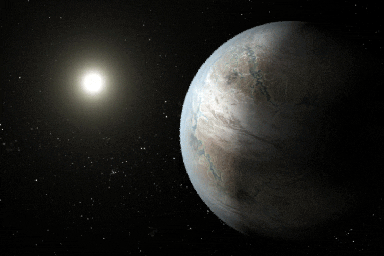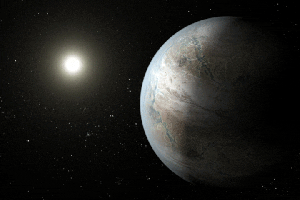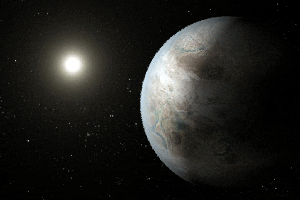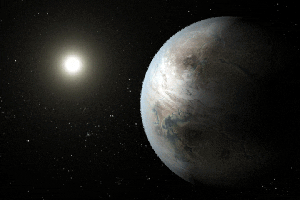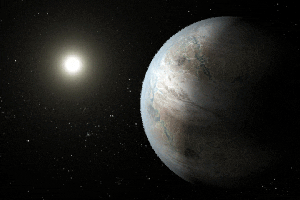
Click for larger animationThis artist's concept depicts one possible appearance of the planet Kepler-452b, the first near-Earth-size world to be found in the habitable zone of star that is similar to our sun. The habitable zone is a region around a star where temperatures are right for water -- an essential ingredient for life as we know it -- to pool on the surface. Scientists do not know if Kepler-452b can support life or not.
What is known about the planet is that it is about 60 percent larger than Earth, placing it in a class of planets dubbed "super-Earths." While its mass and composition are not yet determined, previous research suggests that planets the size of Kepler-452b have a better than even chance of being rocky. Kepler-452b orbits its star every 385 days.
The planet's star is about 1,400 light-years away in the constellation Cygnus. It is a G2-type star like our sun, with nearly the same temperature and mass. This star is 6 billion years old, 1.5 billion years older than our sun. As stars age, they grow in size and give out more energy, warming up their planets over time.
Scientists and artists considered these facts when creating this illustration. If the planet Kepler-452b does in fact have liquid on its surface and has grown warmer due to the older age of its star, it could possibly be experiencing a runaway greenhouse effect, where oceans would begin to evaporate and contribute to increased cloud cover. This, plus other factors such as the planet's large size, was factored into the hypothetical scenario depicted in this illustration.
NASA Ames manages Kepler's ground system development, mission operations and science data analysis. NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, Calif., managed Kepler mission development. Ball Aerospace & Technologies Corp. in Boulder, Colo., developed the Kepler flight system and supports mission operations with JPL at the Laboratory for Atmospheric and Space Physics at the University of Colorado in Boulder. The Space Telescope Science Institute in Baltimore archives, hosts and distributes the Kepler science data. Kepler is NASA's 10th Discovery Mission and is funded by NASA's Science Mission Directorate at the agency's headquarters in Washington.
More information about the Kepler mission is at http://www.nasa.gov/kepler.
More information about exoplanets and NASA's planet-finding program is at http://planetquest.jpl.nasa.gov.

 Planetary Data System
Planetary Data System