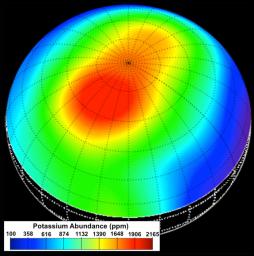
During the first year of MESSENGER's orbital mission, the spacecraft's GRS instrument measured the elemental composition of Mercury's surface materials. Among the most important discoveries from the GRS was the observation of higher abundances of the moderately volatile elements potassium, sodium, and chlorine than expected from previous scientific models and theories. Particularly high concentrations of these elements were observed at high northern latitudes, as illustrated in this potassium abundance map, which provides a view of the surface centered at 60° N latitude and 120° E longitude. This map was the first elemental map ever made of Mercury's surface and is to-date the only map to report absolute elemental concentrations, in comparison to element ratios.
Prior to MESSENGER's arrival at Mercury, scientists expected that the planet would be depleted in moderately volatile elements, as is the case for our Moon. The unexpectedly high abundances observed with the GRS have forced a reevaluation of our understanding of the formation and evolution of Mercury. In addition, the K map provided the first evidence for distinct geochemical terranes on Mercury, as the high-potassium region was later found to also be distinct in its low Mg/Si, Ca/Si, S/Si, and high Na/Si and Cl/Si abundances.
Instrument: Gamma-Ray Spectrometer (GRS)
The MESSENGER spacecraft is the first ever to orbit the planet Mercury, and the spacecraft's seven scientific instruments and radio science investigation are unraveling the history and evolution of the Solar System's innermost planet. In the mission's more than four years of orbital operations, MESSENGER has acquired over 250,000 images and extensive other data sets. MESSENGER's highly successful orbital mission is about to come to an end, as the spacecraft runs out of propellant and the force of solar gravity causes it to impact the surface of Mercury in April 2015.
For information regarding the use of images, see the MESSENGER image use policy.

 Planetary Data System
Planetary Data System