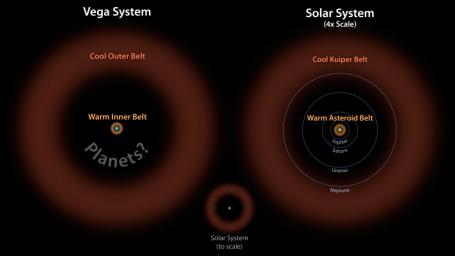
Astronomers have discovered what appears to be a large asteroid belt around the bright star Vega, as illustrated here at left in brown. The ring of warm, rocky debris was detected using NASA's Spitzer Space Telescope, and the European Space Agency's Herschel Space Observatory, in which NASA plays an important role.
In this diagram, the Vega system, which was already known to have a cooler outer belt of comets (orange), is compared to our solar system with its asteroid and Kuiper belts. The relative size of our solar system compared to Vega is illustrated by the small drawing in the middle. On the right, our solar system is scaled up four times.
The comparison illustrates that both systems have inner and outer belts with similar proportions. The gap between the inner and outer debris belts in both systems works out to a ratio of about 1-to-10, with the outer belt 10 times farther away from its host star than the inner belt.
Astronomers think that the gap in the Vega system may be filled with planets, as is the case in our solar system.
JPL manages the Spitzer Space Telescope mission for NASA's Science Mission Directorate, Washington. Science operations are conducted at the Spitzer Science Center at Caltech. Data are archived at the Infrared Science Archive housed at the Infrared Processing and Analysis Center at Caltech.
For more information about Spitzer, visit http://spitzer.caltech.edu and http://www.nasa.gov/spitzer.
Herschel is a European Space Agency cornerstone mission, with science instruments provided by consortia of European institutes and with important participation by NASA. NASA's Herschel Project Office is based at JPL, which contributed mission-enabling technology for two of Herschel's three science instruments. The NASA Herschel Science Center, part of the Infrared Processing and Analysis Center at Caltech, supports the United States astronomical community. More information is online at: http://www.herschel.caltech.edu, http://www.nasa.gov/herschel, and http://www.esa.int/SPECIALS/Herschel/index.html.

 Planetary Data System
Planetary Data System