 |  |
| Annotated Version | Black and White Version |
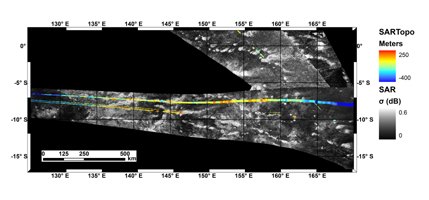
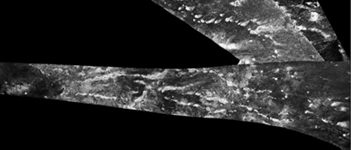
Click on an individual image for larger viewThis mosaic, made from radar images obtained by NASA's Cassini spacecraft, shows parallel mountain chains on Saturn's moon Titan, near an equatorial region known as Adiri. This mosaic focuses on an area around 10 degrees south latitude and 145 degrees east longitude. The annotated version shows topographic profiles obtained by the radar instrument, with red areas showing the highest elevation (in this image, 250 meters above the mean radius of Titan) and purple showing the lowest (in this image, 450 meters below the mean radius of Titan). That version also shows a grid for latitude and longitude.
Scientists believe the structures rose up because the lithosphere, the outermost layer of the surface, folded up during deformation of the outer water ice shell.
Cassini's radar instrument obtained the black-and-white image of the terrain on Feb. 22, and Oct. 28, 2005. In radar images, objects appear bright when they are tilted toward the spacecraft or have rough surfaces. The topographical data were derived from the same flybys.
For another view of this terrain, see PIA03566.
The Cassini-Huygens mission is a cooperative project of NASA, the European Space Agency and the Italian Space Agency. The Jet Propulsion Laboratory, a division of the California Institute of Technology in Pasadena, manages the mission for NASA's Science Mission Directorate. The Cassini orbiter was designed, developed and assembled at JPL. The radar instrument was built by JPL and the Italian Space Agency, working with team members from the United States and several European countries.
For more information about the Cassini-Huygens mission visit http://www.nasa.gov/cassini and http://saturn.jpl.nasa.gov.

