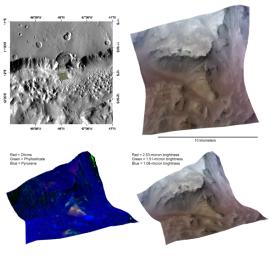
This image of the wall of Capri Chasma, in Valles Marineris, was taken by the Compact Reconnaissance Imaging Spectrometer for Mars (CRISM) at 1151 UTC (7:51 a.m. EDT) on October 6, 2007, near 12.03 degrees south latitude, 312.04 degrees east longitude. CRISM's image was taken in 544 colors covering 0.36-3.92 micrometers, and shows features as small as 20 meters (66 feet) across. The region covered is just over 10 kilometers (6.2 miles) wide at its narrowest point, and is one of several dozen that CRISM has taken to search for exposed layering in the chasma walls.
Valles Marineris is a large canyon system that extends more than 4,000 kilometers (2,485 miles) covering nearly one-fifth of the planet's circumference. If it were located on Earth, Valles Marineris would stretch from the California coast to New England and hold a volume of water approximately equal to that held by the Mediterranean Sea. One of several chasmata that comprise Valles Marineris, Capri Chasma is located toward the eastern end of the larger system.
The upper left panel in the montage above reveals the location of the CRISM image on a mosaic taken by the Mars Odyssey spacecraft's Thermal Emission Imaging System (THEMIS). The CRISM data are centered on a resistant spur of material roughly 4 kilometers (2.5 miles) long, located below a crater whose floor was eroded away by the chasma's rim. The upper right panel reveals this spur in infrared false color. Bright streaks emanating downward from the ridge indicate mass wasting of the lighter material that caps the spur.
The lower two images are renderings of data draped over topography without vertical exaggeration. These images provide a view of the spur's elevation relative to the surrounding terrain - the lower right in infrared false color, the lower left in false color to reveal mineral content. The predominantly blue color of the lower left image shows that the chasma wall rock is rich in pyroxene, a major constituent of basaltic rocks. The reds and greens in the resistant material that comprises the ridge indicate the presence of olivine and clay-like minerals called phyllosilicates. Broad swaths of red, yellow and green indicate mass wasting of this resistant material down the slope of the spur. Occurrence of phyllosilicate in the deep-seated wall rock provides evidence for a very ancient wet environment.
CRISM is one of six science instruments on NASA's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter. Led by The Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory, Laurel, Md., the CRISM team includes expertise from universities, government agencies and small businesses in the United States and abroad. NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory, a division of the California Institute of Technology in Pasadena, manages the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter and the Mars Science Laboratory for NASA's Science Mission Directorate, Washington. Lockheed Martin Space Systems, Denver, built the orbiter.

 Planetary Data System
Planetary Data System