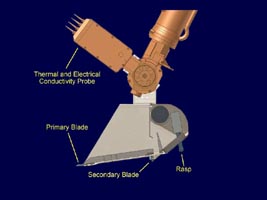
Annotated VersionThis illustration shows some of the components on and near the end of the robotic arm on NASA's Phoenix Mars Lander. Primary and secondary blades on the scoop will aid in the collection of soil samples. A powered rasp will allow the arm to sample an icy layer expected to be about as hard as concrete. The thermal and electrical conductivity probe, which is one part of the Microscopy, Electrochemistry and Conductivity Analyzer, will assess how heat and electrons move through the soil from one spike to another of a four-spike electronic fork that will be pushed into the soil at different stages of digging by the arm.
Photojournal Note: As planned, the Phoenix lander, which landed May 25, 2008 23:53 UTC, ended communications in November 2008, about six months after landing, when its solar panels ceased operating in the dark Martian winter.

