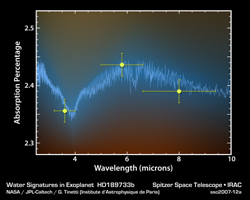
Click on image for larger poster versionThis plot of data from NASA's Spitzer Space Telescope tells astronomers that a toasty gas exoplanet, or a planet beyond our solar system, contains water vapor.
Spitzer observed the planet, called HD 189733b, cross in front of its star at three different infrared wavelengths: 3.6 microns; 4.5 microns and 8 microns (see lime-colored dots). For each wavelength, the planet's atmosphere absorbed different amounts of the starlight that passed through it. The pattern by which this absorption varies with wavelength matches known signatures of water, as shown by the theoretical model in blue.

