During the past two-and-a-half years of traversing the central part of Gusev Crater, NASA's Mars Exploration Rover Spirit has analyzed the brushed and ground-into surfaces of multiple rocks using the alpha particle X-ray spectrometer, which measures the abundance of major chemical elements. In the process, Spirit has documented the first example of a particular kind of volcanic region on Mars known as an alkaline igneous province. The word alkaline refers to the abundance of sodium and potassium, two major rock-forming elements from the alkali metals on the left-hand side of the periodic table.
All of the relatively unaltered rocks -- those least changed by wind, water, freezing, or other weathering agents -- examined by Spirit have been igneous, meaning that they crystallized from molten magmas. One way geologists classify igneous rocks is by looking at the amount of potassium and sodium relative to the amount of silica, the most abundant rock-forming mineral on Earth. In the case of volcanic rocks, the amount of silica present gives scientists clues to the kind of volcanism that occurred, while the amounts of potassium and sodium provide clues about the history of the rock. Rocks with more silica tend to erupt explosively. Higher contents of potassium and sodium, as seen in alkaline rocks like those at Gusev, may indicate partial melting of magma at higher pressure, that is, deeper in the Martian mantle. The abundance of potassium and sodium determines the kinds of minerals that make up igneous rocks. If igneous rocks have enough silica, potassium and sodium always bond with the silica to form certain minerals.
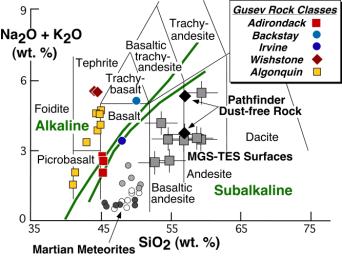
The Gusev rocks define a new chemical category not previously seen on Mars, as shown in this diagram plotting alkalis versus silica, compiled by University of Tennessee geologist Harry McSween. The abbreviations "Na2O" and "K2O" refer to oxides of sodium and potassium. The abbreviation "SiO2" refers to silica. The abbreviation "wt. %" indicates that the numbers tell what percentage of the total weight of each rock is silica (on the horizontal scale) and what percentage is oxides of sodium and potassium (on the vertical scale). The thin lines separate volcanic rock types identified on Earth by different scientific names such as foidite and picrobasalt. Various classes of Gusev rocks (see box in upper right) all plot either on or to the left of the green lines, which define "alkaline" and "subalkaline" categories (subalkaline rocks have more silica than alkaline rocks).
Members of the rover team have named different classes of rocks after specimens examined by Spirit that represent their overall character. During the rover's travels, Spirit discovered that Adirondack-class rocks littered the Gusev plains; that Backstay, Irvine, and Wishstone-class rocks occurred as loose blocks on the northwest slope of "Husband Hill"; and that outcrops of Algonquin-class rocks protruded in several places on the southeast face.
These rocks have less silica than all previously analyzed Mars samples, which are subalkaline. The previously analyzed Mars samples include Martian meteorites found on Earth and rocks analyzed by the Mars Pathfinder rover in 1997. Gusev is the first documented example of an alkaline igneous province on Mars.

 Planetary Data System
Planetary Data System