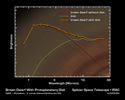
Figure 1This graph of data from NASA's Spitzer Space Telescope shows that an extraordinarily low-mass brown dwarf, or "failed star," is circled by a disc of planet-building dust. The brown dwarf, called OTS 44, is only 15 times the mass of Jupiter, making it the smallest known brown dwarf to host a planet-forming disc.
Spitzer was able to see this unusual disc by measuring its infrared brightness. Whereas a brown dwarf without a disc (red dashed line) radiates infrared light at shorter wavelengths, a brown dwarf with a disc (orange line) gives off excess infrared light at longer wavelengths. This surplus light comes from the disc itself and is represented here as a yellow dotted line. Actual data points from observations of OTS 44 are indicated with orange dots. These data were acquired using Spitzer's infrared array camera.

