Released 16 July 2004
The atmosphere of Mars is a dynamic system. Water-ice clouds, fog, and hazes can make imaging the surface from space difficult. Dust storms can grow from local disturbances to global sizes, through which imaging is impossible. Seasonal temperature changes are the usual drivers in cloud and dust storm development and growth.
Eons of atmospheric dust storm activity has left its mark on the surface of Mars. Dust carried aloft by the wind has settled out on every available surface; sand dunes have been created and moved by centuries of wind; and the effect of continual sand-blasting has modified many regions of Mars, creating yardangs and other unusual surface forms.
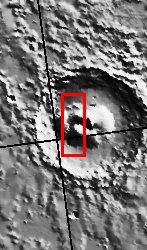
This image illustrates different amounts of yardang development on the large deposit found on the floor of Nicholson Crater. Note the formation of the ridge/trough shape at the bottom part of the main deposit.
Image information: VIS instrument. Latitude 0.2, Longitude 195.3 East (164.7 West). 19 meter/pixel resolution.
Note: this THEMIS visual image has not been radiometrically nor geometrically calibrated for this preliminary release. An empirical correction has been performed to remove instrumental effects. A linear shift has been applied in the cross-track and down-track direction to approximate spacecraft and planetary motion. Fully calibrated and geometrically projected images will be released through the Planetary Data System in accordance with Project policies at a later time.
NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory manages the 2001 Mars Odyssey mission for NASA's Office of Space Science, Washington, D.C. The Thermal Emission Imaging System (THEMIS) was developed by Arizona State University, Tempe, in collaboration with Raytheon Santa Barbara Remote Sensing. The THEMIS investigation is led by Dr. Philip Christensen at Arizona State University. Lockheed Martin Astronautics, Denver, is the prime contractor for the Odyssey project, and developed and built the orbiter. Mission operations are conducted jointly from Lockheed Martin and from JPL, a division of the California Institute of Technology in Pasadena.

