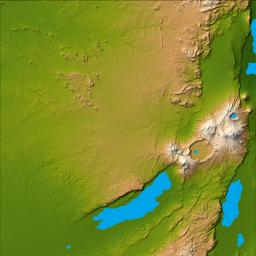
Three striking and important areas of Tanzania in eastern Africa are shown in this color-coded shaded relief image from the Shuttle Radar Topography Mission. The largest circular feature in the center right is the caldera, or central crater, of the extinct volcano Ngorongoro. It is surrounded by a number of smaller volcanoes, all associated with the Great Rift Valley, a geologic fault system that extends for about 4,830 kilometers (2,995 miles) from Syria to central Mozambique.
Ngorongoro's caldera is 22.5 kilometers (14 miles) across at its widest point and is 610 meters (2,000 feet) deep. Its floor is very level, holding a lake fed by streams running down the caldera wall. It is part of the Ngorongoro Conservation Area and is home to over 75,000 animals. The lakes south of the crater are Lake Eyasi and Lake Manyara, also part of the conservation area.
The relatively smooth region in the upper left of the image is the Serengeti National Park, the largest in Tanzania. The park encompasses the main part of the Serengeti ecosystem, supporting the greatest remaining concentration of plains game in Africa including more than 3,000,000 large mammals. The animals roam the park freely and in the spectacular migrations, huge herds of wild animals move to other areas of the park in search of greener grazing grounds (requiring over 4,000 tons of grass each day) and water.
The faint, nearly horizontal line near the center of the image is Olduvai Gorge, made famous by the discovery of remains of the earliest humans to exist. Between 1.9 and 1.2 million years ago a salt lake occupied this area, followed by the appearance of fresh water streams and small ponds. Exposed deposits show rich fossil fauna, many hominid remains and items belonging to one of the oldest stone tool technologies, called Olduwan. The time span of the objects recovered dates from 2,100,000 to 15,000 years ago.
Two visualization methods were combined to produce the image: shading and color coding of topographic height. The shade image was derived by computing topographic slope in the northwest-southeast direction, so that northwest slopes appear bright and southeast slopes appear dark. Color coding is directly related to topographic height, with green at the lower elevations, rising through yellow and tan, to white at the highest elevations.
Elevation data used in this image were acquired by the Shuttle Radar Topography Mission aboard the Space Shuttle Endeavour, launched on Feb. 11, 2000. SRTM used the same radar instrument that comprised the Spaceborne Imaging Radar-C/X-Band Synthetic Aperture Radar (SIR-C/X-SAR) that flew twice on the Space Shuttle Endeavour in 1994. SRTM was designed to collect 3-D measurements of the Earth's surface. To collect the 3-D data, engineers added a 60-meter (approximately 200-foot) mast, installed additional C-band and X-band antennas, and improved tracking and navigation devices. The mission is a cooperative project between NASA, the National Geospatial-Intelligence Agency (NGA) of the U.S. Department of Defense and the German and Italian space agencies. It is managed by NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Pasadena, Calif., for NASA's Earth Science Enterprise, Washington, D.C.
Location: 3 degrees south latitude, 35 degrees east longitude
Orientation: North toward the top, Mercator projection
Size: 223 by 223 kilometers (138 by 138 miles)
Image Data: shaded and colored SRTM elevation model
Date Acquired: February 2000

 Planetary Data System
Planetary Data System