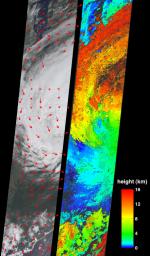
On Tuesday, August 30, 2005, NASA's Multi-angle Imaging SpectroRadiometer retrieved cloud-top heights and cloud-tracked wind velocities for Tropical Storm Katrina, as the center of the storm was situated over the Tennessee valley. At this time Katrina was weakening and no longer classified as a hurricane, and would soon become an extratropical depression. Measurements such as these can help atmospheric scientists compare results of computer-generated hurricane simulations with observed conditions, ultimately allowing them to better represent and understand physical processes occurring in hurricanes.
Because air currents are influenced by the Coriolis force (caused by the rotation of the Earth), Northern Hemisphere hurricanes are characterized by an inward counterclockwise (cyclonic) rotation towards the center. It is less widely known that, at high altitudes, outward-spreading bands of cloud rotate in a clockwise (anticyclonic) direction. The image on the left shows the retrieved cloud-tracked winds as red arrows superimposed across the natural color view from MISR's nadir (vertical-viewing) camera. Both the counter-clockwise motion for the lower-level storm clouds and the clockwise motion for the upper clouds are apparent in these images. The speeds for the clockwise upper level winds have typical values between 40 and 45 m/s (144-162 km/hr). The low level counterclockwise winds have typical values between 7 and 24 m/s (25-86 km/hr), weakening with distance from the storm center. The image on the right displays the cloud-top height retrievals. Areas where cloud heights could not be retrieved are shown in dark gray. Both the wind velocity vectors and the cloud-top height field were produced by automated computer recognition of displacements in spatial features within successive MISR images acquired at different view angles and at slightly different times.
The Multi-angle Imaging SpectroRadiometer observes the daylit Earth continuously, viewing the entire globe between 82° north and 82° south latitude every nine days. This image covers an area of about 380 kilometers by 1970 kilometers. These data products were generated from a portion of the imagery acquired during Terra orbit 30324 and utilize data from blocks 55-68 within World Reference System-2 path 22.
MISR was built and is managed by NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Pasadena, CA, for NASA's Science Mission Directorate, Washington, DC. The Terra satellite is managed by NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center, Greenbelt, MD. JPL is managed for NASA by the California Institute of Technology.

 Planetary Data System
Planetary Data System