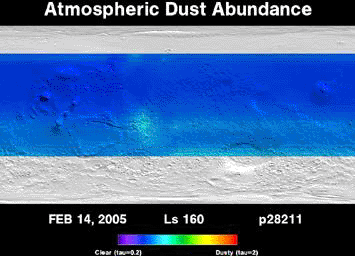
AnimationThis movie shows the daily abundance of dust in the martian atmosphere over a period of three full martian years, from April 1999 through February 2005. The Thermal Emission Spectrometer instrument on NASA's Mars Global Surveyor orbiter has been tracking the weather on Mars for six years. The infrared spectrum observed by this instrument yields information about the spectral properties of the dust and the temperature of the atmosphere. These two properties can then be used to derive how much dust is in the atmosphere.
Of particular interest are large regional and global dust storms that occur during summer in the southern hemisphere each Mars year. The 2001 storm was by far the largest, lasting over six months (June to October, 2001) and covering the entire planet. The storms in the other two Mars years shown here were much smaller and never covered the planet. The most recent storm season (June 2003 through January 2005) actually had two separate storms, one in June and a second in December. Unlike most large martian dust storms that start in the southern hemisphere, the December storm began in the north and swept toward the equator. Between storms the atmosphere becomes quite clear, with much smaller dust storms scattered throughout the year and over the planet.
Seasons on Mars are determined by the position of Mars in its orbit around the Sun. The position is measured in degrees of solar longitude (Ls) around the orbit, beginning at 0 degrees Ls at the northern spring equinox, progressing to 90 degrees Ls at the start of northern summer, 180 degrees Ls at the fall equinox, 270 degrees Ls at the start of northern winter, and finally back to 360 degrees, or 0 degrees, Ls at the spring equinox. Dust abundance is measured as opacity (tau), with values of 0 tau representing a completely clear atmosphere, and values of 2 indicating that it is nearly impossible to see through to the surface.
The Thermal Emission Spectrometer is operated by a team led at Arizona State University, Tempe. Mars Global Surveyor left Earth on Nov. 7, 1996, and began orbiting Mars on Sept. 12, 1997. JPL, a division of the California Institute of Technology, Pasadena, manages Mars Global Surveyor for NASA's Science Mission Directorate, Washington.

 Planetary Data System
Planetary Data System