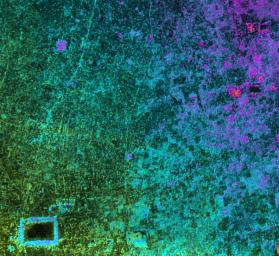
This image of Cambodia's Angkor region, taken by NASA's Airborne Synthetic Aperture Radar (AIRSAR), reveals a temple (upper-right) not depicted on early 19th Century French archeological survey maps and American topographic maps. The temple, known as "Sman Teng," was known to the local Khmer people, but had remained unknown to historians due to the remoteness of its location. The temple is thought to date to the 11th Century: the heyday of Angkor. It is an important indicator of the strategic and natural resource contributions of the area northwest of the capitol, to the urban center of Angkor. Sman Teng, the name designating one of the many types of rice enjoyed by the Khmer, was "discovered" by a scientist at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Pasadena, Calif., working in collaboration with an archaeological expert on the Angkor region. Analysis of this remote area was a true collaboration of archaeology and technology. Locating the temple of Sman Teng required the skills of scientists trained to spot the types of topographic anomalies that only radar can reveal.
This image, with a pixel spacing of 5 meters (16.4 feet), depicts an area of approximately 5 by 4.7 kilometers (3.1 by 2.9 miles). North is at top. Image brightness is from the P-band (68 centimeters, or 26.8 inches) wavelength radar backscatter, a measure of how much energy the surface reflects back toward the radar. Color is used to represent elevation contours. One cycle of color represents 25 meters (82 feet) of elevation change, so going from blue to red to yellow to green and back to blue again corresponds to 25 meters (82 feet) of elevation change.
AIRSAR flies aboard a NASA DC-8 based at NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center, Edwards, Calif. In the TOPSAR mode, AIRSAR collects radar interferometry data from two spatially separated antennas (2.6 meters, or 8.5 feet). Information from the two antennas is used to form radar backscatter imagery and to generate highly accurate elevation data. Built, operated and managed by JPL, AIRSAR is part of NASA's Earth Science Enterprise program. JPL is a division of the California Institute of Technology in Pasadena.

 Planetary Data System
Planetary Data System