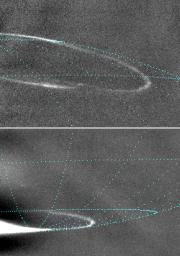
Oval-shaped auroras glow in night-side areas near Jupiter's north and south poles in these images taken by NASA's Cassini spacecraft on Jan. 13, 2001. The lower frame is the first to capture the southern aurora on the planet's night side. Blue lines of longitude and latitude have been added in each frame to indicate position of the glows.
Jupiter's auroral ovals are similar to Earth's auroras, often called the northern lights or southern lights, although fluctuations in solar activity play a more important role in the auroras at Earth than at Jupiter. Energetic particles are constantly streaming towards Jupiter on magnetic field lines that intersect the planet's atmosphere on a ring around the magnetic pole. Where the energetic particles hit the upper atmosphere, they cause emission of light, similar to the glow in a fluorescent bulb. In the north (upper image), the magnetic pole is offset from the rotational pole, which is where the blue longitude lines converge, just to the left of the imaged area. The auroral oval appears like a draped necklace that is carried around by the rotation of the planet. In the south (lower image), the magnetic and rotational poles are nearly coincident, so no significant offset is visible.
Cassini had passed its closest to Jupiter about two weeks before taking these pictures, so it was in position to see the night side of the planet. It was about 16.5 million kilometers (10.3 million miles) from the planet and about 2.5 degrees below the plane of Jupiter's equator. The smallest features visible are about 100 kilometers (about 60 miles) across. The images were taken by Cassini's narrow-band camera through a filter centered on a light-wave frequency at which hydrogen emits light when it is excited. They have been processed to remove scattered light from the overexposed sunlit crescent of the planet. Hydrogen is a major ingredient of Jupiter's atmosphere.
It is not understood why the auroral oval rings are so thin. Cassini images will help scientists figure out what brings about the narrow nature and other features of the auroras, such as the break in the northern oval visible in the upper image.
Cassini is a cooperative project of NASA, the European Space Agency and the Italian Space Agency. The Jet Propulsion Laboratory, a division of the California Institute of Technology in Pasadena, manages the Cassini mission for NASA's Office of Space Science, Washington, D.C.

 Planetary Data System
Planetary Data System