- Original Caption Released with Image:
-
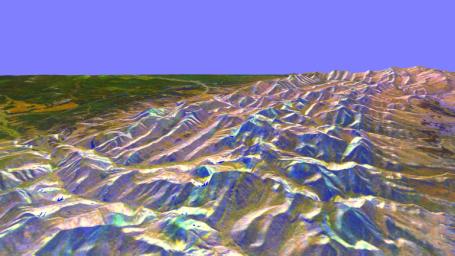
This is a three-dimensional perspective of the eastern front range of the Rocky Mountains, about 120 kilometers (75 miles) west of Great Falls, Montana. The image was created by combining two spaceborne radar images using a technique known as interferometry. Visualizations like this are useful to scientists because they show the shapes of the topographic features such as mountains and valleys. This technique helps to clarify the relationships of the different types of materials on the surface detected by the radar. The view is looking south-southeast. Along the right edge of the image is the valley of the north fork of the Sun River. The western edge of the Great Plains appears on the left side. The valleys in the lower center, running off into the plains on the left, are branches of the Teton River. The highest mountains are at elevations of 2,860 meters (9,390 feet), and the plains are about 1,400 meters (4,500 feet) above sea level. The dark brown areas are grasslands, bright green areas are farms, light brown, orange and purple areas are scrub and forest, and bright white and blue areas are steep rocky slopes.
The two radar images were taken on successive days by the Spaceborne Imaging Radar-C/X-band Synthetic Aperture Radar (SIR-C/X-SAR) on board the space shuttle Endeavour in October 1994. The digital elevation map was produced using radar interferometry, a process in which radar data are acquired on different passes of the space shuttle. The two data passes are compared to obtain elevation information. Radar image data are draped over the topography to provide the color with the following assignments: red is L-band vertically transmitted, vertically received; green is C-band vertically transmitted, vertically received; and blue are the differences seen in the L-band data between the two days. This image is centered near 47.7 degrees north latitude and 112.7 degrees west longitude. No vertical exaggeration factor has been applied to the data. SIR-C/X-SAR, a joint mission of the German, Italian and United States space agencies, is part of NASA's program entitled Mission to Planet Earth.
- Image Credit:
-
NASA/JPL
Image Addition Date: -
1999-04-15
|

 Planetary Data System
Planetary Data System