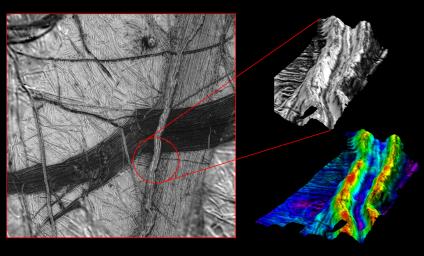
These images reveal the dramatic topography of Europa's icy crust. North is to the right. An east-west running double ridge with a deep intervening trough cuts across older background plains and the darker wedge shaped band. The numerous cracks and bands of such terrain may indicate where the crust has pulled apart and sometimes allowed dark material from beneath the surface to well up and fill the cracks. A computer generated three dimensional perspective (upper right) shows that bright material, probably pure water ice, prevails at the ridge crests and slopes while most dark material (perhaps ice mixed with silicates or hydrated salts) is confined to lower areas such as valley floors. The northernmost (right) slope which faces north, however, has a larger concentration of dark material than south facing slopes. The model on the lower right has been color coded to accentuate elevations. The red tones indicate that the crests of the ridge system reach elevations of more than 300 meters (330 yards) above the surrounding furrowed plains (blue and purple tones). The two ridges are separated by a valley about 1.5 kilometers (0.9 miles) wide.
The stereo perspective combines high resolution images obtained from two different viewing angles. Such a three dimensional model is similar to the three dimensional scenes our brains construct when both eyes view something from two angles.
North is to the right, and the sun illuminates the scene from northwest. The images were taken by the Solid State Imaging (SSI) system on NASA's Galileo spacecraft. The regional context (left), centered at about 16 degrees south latitude, 195 degrees west longitude, was imaged on November 6th, 1996 at a range of about 41,000 kilometers (25,500 miles). The higher resolution stereo images were taken on December 16th, 1997, at ranges of 5,800 kilometers (3,600 miles) and 2,600 kilometers (1,600 miles) leading to a best resolution of 26 meters per picture element.
The Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Pasadena, CA manages the Galileo mission for NASA's Office of Space Science, Washington, DC.
This image and other images and data received from Galileo are posted on the World Wide Web, on the Galileo mission home page at URLhttp://solarsystem.nasa.gov/galileo/. Background information and educational context for the images can be found at URLhttp://www.jpl.nasa.gov/galileo/sepo.

 Planetary Data System
Planetary Data System