The schematic structures of Jupiter's main and gossamer rings are depicted here. Scientists studying data from NASA's Galileo spacecraft have found that the ring system is made up of impact debris created when meteoroids, which are fragments of comets and asteroids, slam into Jupiter's four smallest satellites.
The top panel shows that the main ring (red) is formed mostly from meteoroid impact debris kicked up from the innermost moons, Metis (m) and Adrastea (a). Since both satellites orbit in paths not inclined to Jupiter's equator, the main ring appears as a narrow line.
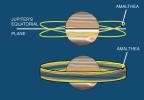
The middle panel shows the additional effect of dust ejected from the satellite Amalthea (A), responsible for producing one of the two moon components of the gossamer ring. Amalthea's orbit is inclined to Jupiter's equatorial plane, and at different times the satellite's vertical position can range anywhere between the two extreme limits shown. Dust ejected from Amalthea (orange) produces a ring whose thickness equals Amalthea's vertical projections beyond Jupiter's equatorial plane.
Satellite Interactions with Jupiter's Ring System
The lower panel shows the additional effect of dust ejected from Thebe (T), which makes up the second component (shown in green) of the gossamer ring. Again, the two positions shown represent the maximum projections of Thebe from Jupiter's equatorial plane. This component of the gossamer ring is thicker than the component due to Amaltheas dust because Thebe's orbit is more inclined than that of Amalthea.
The Jupiter image was created from a map based on data obtained by the Hubble Space Telescope.
JPL manages the Galileo mission for NASA's Office of Space Science, Washington, DC.
The images are posted on the Internet at https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/ and at http://solarsystem.nasa.gov/galileo/. Background information and educational context for the images can be found at: http://www.jpl.nasa.gov/galileo/sepo.

 Planetary Data System
Planetary Data System













