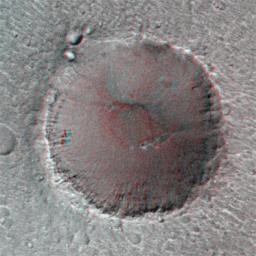
On its 256th orbit of Mars, the camera on-board the Mars Global Surveyor spacecraft successfully observed the vicinity of the Pathfinder landing site. The images shown are a stereoscopic image pair in anaglyph format, made from the overlapping area of MOC 25603 and 23703. This image is reproduced at a scale of 5 m (16.4 feet) per pixel. Image 23703 was acquired on 13 April at 7:50 AM PDT; Image 25603 was acquired on 22 April at 1:11 PM PDT. The P237 observation was made from a distance of 675 km while the P256 measurement was made from 800 km. The viewing angle for 23703 was 21.2°, for 25603, 30.67°, giving an angular difference of about 9.5°. Owing to the relief on "Big Crater," this relatively small angular difference was in this case sufficient to show good stereo parallax.
The resolution of the MOC image that covered the Pathfinder landing site (MOC 25603) was about 3.3 m or 11 feet per pixel. The Pathfinder lander and airbags form a roughly equilateral triangle 5 m on a side. Noting that the camera has not yet been focussed (it needs to be in the stable temperature conditions of the low altitude, circular mapping orbit in order to achieve best focus) and the hazy atmospheric conditions, the effective scale of the image is probably closer to 5 m (16.4 feet). Thus, the scale of the image was insufficient to resolve the lander (more than one pixel is needed to resolve a feature). In addition, the relatively high sun angle of the image (the sun was 40° above the horizon) reduced the length of shadows (for example, only a few boulders are seen), also decreasing the ability to discriminate small features. Work continues to locate intermediate-scale features in the lander and orbiter images in the hope of identifying the precise landing site based on these comparisons.
Malin Space Science Systems and the California Institute of Technology built the MOC using spare hardware from the Mars Observer mission. MSSS operates the camera from its facilities in San Diego, CA. The Jet Propulsion Laboratory's Mars Surveyor Operations Project operates the Mars Global Surveyor spacecraft with its industrial partner, Lockheed Martin Astronautics, from facilities in Pasadena, CA and Denver, CO.

 Planetary Data System
Planetary Data System