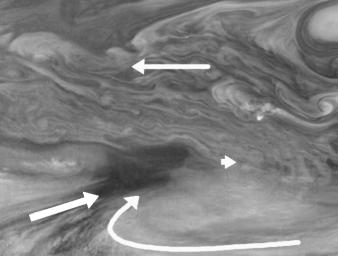
Wind patterns of Jupiter's equatorial region. This mosaic covers an area of 34,000 kilometers by 22,000 kilometers and was taken using the 756 nanometer (nm) near-infrared continuum filter. The dark region near the center of the mosaic is an equatorial "hotspot" similar to the Galileo Probe entry site. The near-infrared continuum filter shows the features of Jupiter's main visible cloud deck.
Jupiter's atmospheric circulation is dominated by alternating jets of east/west (zonal) winds. The bands have different widths and wind speeds but have remained constant as long as telescopes and spacecraft have measured them. The top half of these mosaics lies within Jupiter's North Equatorial Belt, a westward (left) current. The bottom half shows part of the Equatorial Zone, a fast moving eastward current. The clouds near the hotspot are the fastest moving features in these mosaics, moving at about 100 meters per second, or 224 miles per hour.
Superimposed on the zonal wind currents is the Jovian "weather." The arrows show the winds measured by an observer moving eastward (right) at the speed of the hotspot. (The observer's perspective is that the hotspot is "still" while the rest of the planet moves around it.) Clouds south of the hotspot appear to be moving towards it, as seen in the flow aligned with cloud streaks to the southwest and in the clockwise flow to the southeast. Interestingly, there is little cloud motion away from the hotspot in any direction. This is consistent with the idea that dry air is converging over this region and sinking, maintaining the cloud-free nature of the hotspot.
North is at the top. The mosaic covers latitudes 1 to 19 degrees and is centered at longitude 336 degrees West. The smallest resolved features are tens of kilometers in size. These images were taken on December 17, 1996, at a range of 1.5 million kilometers by the Solid State Imaging system aboard NASA's Galileo spacecraft.
The Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Pasadena, CA manages the mission for NASA's Office of Space Science, Washington, DC.
This image and other images and data received from Galileo are posted on the World Wide Web, on the Galileo mission home page at URL http://galileo.jpl.nasa.gov. Background information and educational context for the images can be found at http://www.jpl.nasa.gov/galileo/sepo.

 Planetary Data System
Planetary Data System