Gully landforms proposed to have been caused by geologically-recent seepage and runoff of liquid water on Mars are found in the most unlikely places. They typically occur in areas that are quite cold -- well below freezing -- all year round. Like the old adage about moss on trees, nearly all of them form on slopes that face away from sunlight. Most of the gullies occur at latitudes between 30° and 70°.
The highest latitude at which martian gullies have been found is around 70°-75°S on the walls of pits developed in the south polar pitted plains. If you were at this same latitude on Earth, you would be in Antarctica. This region spends much of the winter -- which lasts approximately 6 months on Mars -- in darkness and at temperatures cold enough to freeze carbon dioxide (around -130°C or -200°F). Nevertheless, gullies with very sharp, deep, v-shaped channels are seen on the pit walls (above, left).
Based upon the locations of the tops of the channels on the slope shown here, the inferred site of liquid seepage is located at a layer in the pit wall about 1/3 of the way down from the top of the MOC image. The channels start wide and taper downslope. The area above the channels is layered and has been eroded by mass movement -- dry avalanching of debris -- to form a pattern of chutes and ridges on the upper slope of the pit wall. The top layer appears to have many boulders in it (each about the size of a small house), these boulders are left behind on the upper slopes of the pit wall as debris is removed.
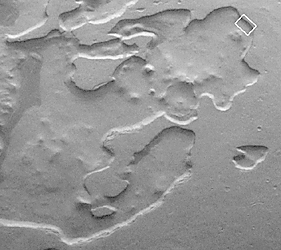
Centered near 70.7°S, 355.7°W, the MOC image was acquired July 14, 1999, and covers an area approximately 2.8 km (1.7 mi) wide by 2.1 km (1.3 mi) high. Sunlight illuminates the MOC image from the upper left and north is toward the upper left. The context view (right) is from the Viking 2 orbiter and was acquired in 1977. The Viking picture is illuminated from the top/upper left; north is toward the upper right. The small white box in the context frame (upper right corner) shows the location of the high resolution MOC view.

