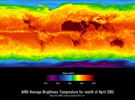
Figure 1This image shows average temperatures in April, 2003, observed by AIRS at an infrared wavelength that senses either the Earth's surface or any intervening cloud. Similar to a photograph of the planet taken with the camera shutter held open for a month, stationary features are captured while those obscured by moving clouds are blurred. Many continental features stand out boldly, such as our planet's vast deserts, and India, now at the end of its long, clear dry season. Also obvious are the high, cold Tibetan plateau to the north of India, and the mountains of North America. The band of yellow encircling the planet's equator is the Intertropical Convergence Zone (ITCZ), a region of persistent thunderstorms and associated high, cold clouds. The ITCZ merges with the monsoon systems of Africa and South America. Higher latitudes are increasingly obscured by clouds, though some features like the Great Lakes, the British Isles and Korea are apparent. The highest latitudes of Europe and Eurasia are completely obscured by clouds, while Antarctica stands out cold and clear at the bottom of the image.
About AIRS
The Atmospheric Infrared Sounder, AIRS, in conjunction with the Advanced Microwave Sounding Unit, AMSU, senses emitted infrared and microwave radiation from Earth to provide a three-dimensional look at Earth's weather and climate. Working in tandem, the two instruments make simultaneous observations all the way down to Earth's surface, even in the presence of heavy clouds. With more than 2,000 channels sensing different regions of the atmosphere, the system creates a global, three-dimensional map of atmospheric temperature and humidity, cloud amounts and heights, greenhouse gas concentrations, and many other atmospheric phenomena. Launched into Earth orbit in 2002, the AIRS and AMSU instruments fly onboard NASA's Aqua spacecraft and are managed by NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, Calif., under contract to NASA. JPL is a division of the California Institute of Technology in Pasadena.
More information about AIRS can be found at http://airs.jpl.nasa.gov.

