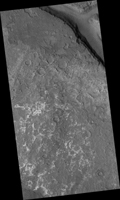
Map Projected Browse Image
Click on the image for larger versionLadon Basin was a large impact structure that was filled in by the deposits from Ladon Valles, a major ancient river on Mars as seen in this image from NASA's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO).
These wet sediments were altered into minerals such as various clay minerals. Clays imply chemistry that may have been favorable for life on ancient Mars, if anything lived there, so this could be a good spot for future exploration by rovers and perhaps return of samples to Earth.
The map is projected here at a scale of 50 centimeters (19.7 inches) per pixel. [The original image scale is 52.1 centimeters (20.5 inches) per pixel (with 2 x 2 binning); objects on the order of 156 centimeters (61.4 inches) across are resolved.] North is up.
The University of Arizona, Tucson, operates HiRISE, which was built by Ball Aerospace & Technologies Corp., Boulder, Colorado. NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory, a division of Caltech in Pasadena, California, manages the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter Project for NASA's Science Mission Directorate, Washington.

