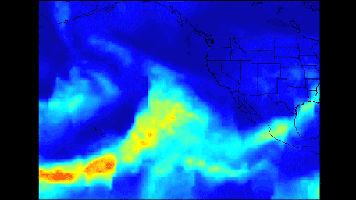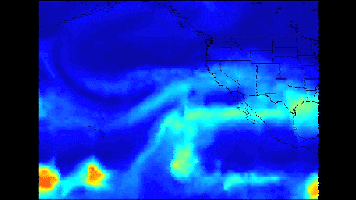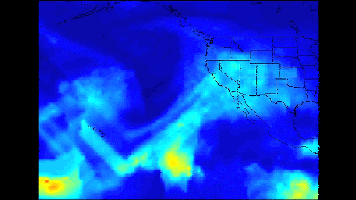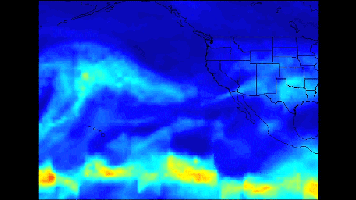
Click on the image for larger animationA series of atmospheric rivers that brought drought-relieving rains, heavy snowfall and flooding to California this week is highlighted in a new movie created with satellite data from the Atmospheric Infrared Sounder (AIRS) instrument on NASA's Aqua satellite.
The images of atmospheric water vapor were collected by AIRS between January 7 and 11. They show the amount of moisture present in the atmosphere and its movement across the Pacific Ocean to the United States, where much of it fell as rain or snow.
In early January 2017, the Western U.S. experienced rain and flooding from a series of storms flowing to America on multiple streams of moist air, each individually known as an atmospheric river. Atmospheric rivers are typically 250 to 375 miles (400 to 600 kilometers) wide. The term "Pineapple Express" refers to atmospheric rivers that originate near or just east of the Hawaiian Islands and terminate along the West Coast of North America. Other atmospheric rivers originate in the tropical Western Pacific Ocean and take on a more west-to-east orientation near the U.S. West Coast.
Several distinct plumes of moisture are apparent in the AIRS imagery. The first of three atmospheric river events occurred on January 7 and 8. This was a classic Pineapple Express, featuring an uninterrupted supply of heavy moisture drawn up from the deep tropics. This was the wettest storm of the series, producing very heavy rainfall, more than 1 foot (0.3 meter), in parts of Central and Northern California, with relatively smaller amounts of snow at the highest elevations of the Sierra Nevada.
The second blob of heavy moisture, from January 8 to 10 to the west of California, likely originated thousands of miles to the west, in the tropical Western Pacific. This atmospheric river did not maintain its tropical connection. However, it still produced prodigious rainfall totals in Northern California and much more snow than the first event, since the storm had a more northern and colder trajectory.
A third storm, the coldest of the three events, moved through California on January 11 and 12, producing significant rainfall, as well as snow at higher elevations.
The movie ends with another atmospheric river attempting to form on January 11 and 12 to the west of Hawaii, transporting moisture into the storm track.
About AIRS
The Atmospheric Infrared Sounder, AIRS, in conjunction with the Advanced Microwave Sounding Unit, AMSU, senses emitted infrared and microwave radiation from Earth to provide a three-dimensional look at Earth's weather and climate. Working in tandem, the two instruments make simultaneous observations all the way down to Earth's surface, even in the presence of heavy clouds. With more than 2,000 channels sensing different regions of the atmosphere, the system creates a global, three-dimensional map of atmospheric temperature and humidity, cloud amounts and heights, greenhouse gas concentrations, and many other atmospheric phenomena. Launched into Earth orbit in 2002, the AIRS and AMSU instruments fly onboard NASA's Aqua spacecraft and are managed by NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, California, under contract to NASA. JPL is a division of the California Institute of Technology in Pasadena.
More information about AIRS can be found at airs.jpl.nasa.gov.

