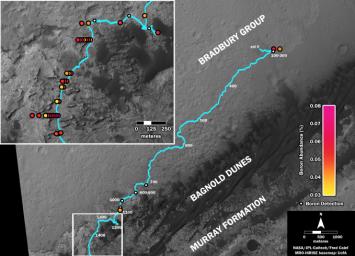
This map shows the route driven by NASA's Curiosity Mars rover (blue line) and locations where the rover's Chemistry and Camera (ChemCam) instrument detected the element boron (dots, colored by abundance of boron according to the key at right).
The main map shows the traverse from landing day (Sol 0) in August 2012 to the rover's location in September 2016, with boron detections through September 2015. The inset at upper left shows a magnified version of the most recent portion of that traverse, with boron detections during that portion. Overlapping dots represent cases when boron was detected in multiple ChemCam observation points in the same target and non-overlapping dots represent cases where two different targets in the same location have boron.
Most of the mission's detections of boron have been made in the most recent seven months (about 200 sols) of the rover's uphill traverse.
The base image for the map is from the High Resolution Imaging Science Experiment (HiRISE) camera on NASA's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter. North is up. The scale bar at lower right represents one kilometer (0.62 mile).
Presented at the 2016 AGU Fall Meeting on Dec. 13. in San Francisco, CA.
ChemCam is one of 10 instruments in Curiosity's science payload. The U.S. Department of Energy's Los Alamos National Laboratory, in Los Alamos, New Mexico, developed ChemCam in partnership with scientists and engineers funded by the French national space agency (CNES), the University of Toulouse and the French national research agency (CNRS). More information about ChemCam is available at http://www.msl-chemcam.com/.
NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory, a division of Caltech in Pasadena, California, manages the Mars Science Laboratory Project and Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter Project for NASA's Science Mission Directorate, Washington.
For more information about Curiosity, visit http://www.nasa.gov/msl and http://mars.jpl.nasa.gov/msl.

 Planetary Data System
Planetary Data System