Map Projected Browse Image
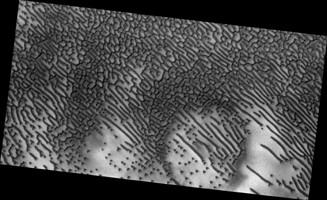
Click on the image for larger versionThese dark dunes are influenced by local topography. The shape and orientation of dunes can usually tell us about wind direction, but in this image, the dune-forms are very complex, so it's difficult to know the wind direction.
However, a circular depression (probably an old and infilled impact crater) has limited the amount of sand available for dune formation and influenced local winds. As a result, the dunes here form distinct dots and dashes. The "dashes" are linear dunes formed by bi-directional winds, which are not traveling parallel to the dune. Instead, the combined effect of winds from two directions at right angles to the dunes, funnels material into a linear shape. The smaller "dots" (called "barchanoid dunes") occur where there is some interruption to the process forming those linear dunes. This process is not well understood at present and is one motivation for HiRISE to image this area.
This is a stereo pair with ESP_045334_2580.
The University of Arizona, Tucson, operates HiRISE, which was built by Ball Aerospace & Technologies Corp., Boulder, Colo. NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory, a division of the California Institute of Technology in Pasadena, manages the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter Project for NASA's Science Mission Directorate, Washington.

