Annotated Image
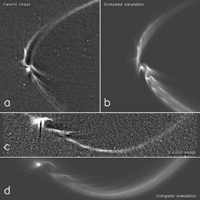
Click on the image for larger versionThis collage, consisting of two Cassini images of long, sinuous, tendril-like features from Saturn's moon Enceladus and two corresponding computer simulations of the same features, illustrates how well the structures, and the sizes of the particles composing them, can be modeled by tracing the trajectories of tiny, icy grains ejected from Enceladus' south polar geysers.
The figures labeled "a" and "c" (see annotated image above) are computer-enhanced images of the tendril structures near Enceladus that were taken at high solar phase angle (174 and 170 degrees, respectively); figures "b" and "d" are synthetic (computer-generated) images produced by following the trajectories of tiny, icy particles ejected from the 36 most active geysers (representing the top 50 percent of the moon's total geysering activity) found on the south polar terrain. The match between real and synthetic images is quite good and strongly supports the suggestion that tendrils are produced by the moon's geysers.
Electromagnetic effects associated with electrical charges that collect on small grains embedded in a magnetosphere like Saturn's can modify the grains' trajectories. These effects are very sensitive to particle size, with smaller particles feeling the effects of charging more strongly than larger ones. The scale of the arc-like structures seen in the tendrils allows scientists to determine that the tendril particles are no smaller than about 0.5 microns (a micron is one millionth of a meter), a size consistent with that of E-ring particles found from other Cassini observations, both imaging and in situ.
Figure "a" is from the observation of 2006; "c" was taken on July 19, 2013 during Cassini's Earth-imaging event (see PIA17172). Orbital motion is counter-clockwise in all images.
The Cassini mission is a cooperative project of NASA, ESA (the European Space Agency) and the Italian Space Agency. The Jet Propulsion Laboratory, a division of the California Institute of Technology in Pasadena, manages the mission for NASA's Science Mission Directorate, Washington. The Cassini orbiter and its two onboard cameras were designed, developed and assembled at JPL. The imaging operations center is based at the Space Science Institute in Boulder, Colorado.
For more information about the Cassini-Huygens mission visit http://saturn.jpl.nasa.gov and http://www.nasa.gov/cassini. The Cassini imaging team homepage is at http://ciclops.org.

