Annotated Version
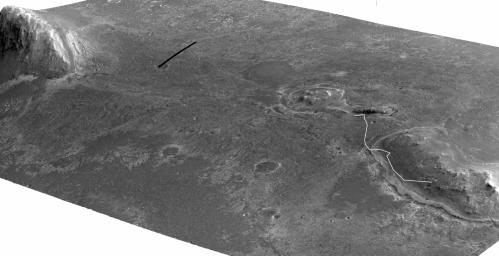
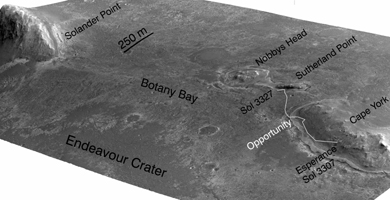
Click on the image for larger versionA stereo pair of images from taken from Mars orbit were used to generate a digital elevation model that is the basis for this simulated perspective view of "Cape York," "Botany Bay," and "Solander Point" on the western rim of Endeavour Crater. The view is from the crater interior looking toward the southwest, and the vertical exaggeration is fivefold.
NASA's Mars Exploration Rover Opportunity investigated the Cape York segment of Endeavour's rim from August 2011 to May 2013 and then drove away from Cape York toward Solander Point. A white line labeled "Opportunity" indicates the rover's traverse from a target called "Esperance" on Cape York to the rover's location on 3,327th sol (Martian day) of the rover's mission on Mars (June 3, 2013).
The High Resolution Imaging Science Experiment (HiRISE) camera on NASA's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter took the images used for creating this elevation model and simulated perspective view.
For reference, the highest elevation on Solander Point is approximately 180 feet (55 meters) above the surrounding plains. Opportunity is on the way to the northern tip of Solander Point to spend the upcoming winter season. That location has a north-facing slope favorable for electrical output by Opportunity's solar panels during the Mars southern-hemisphere winter. Researchers expect that tens of yards, or meters, of ancient strata uplifted by or deposited during the formation of Endeavour Crater will be exposed for detailed measurements.
Ohio State University, Columbus, generated the digital elevation model using HiRISE frames catalogued as PSP_018701_1775_red.jp2 and PSP_018846_1775_red. jp2. The University of Arizona, Tucson, operates HiRISE. NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory, a division of the California Institute of Technology, Pasadena, manages the Mars Exploration Rover and Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter projects for NASA's Science Mission Directorate, Washington.

 Planetary Data System
Planetary Data System