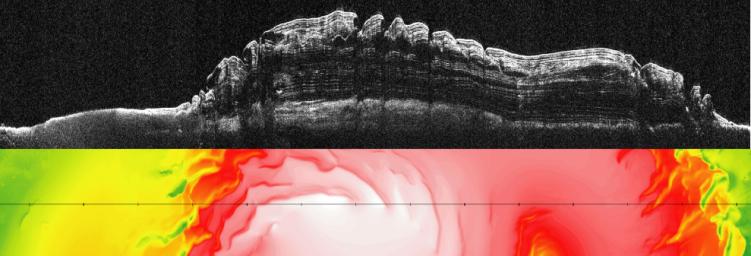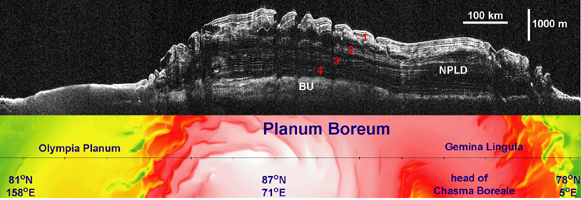
Click on image for larger annotated versionThis image (top) taken by the Shallow Radar instrument on NASA's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter reveals the layers of ice, sand and dust that make up the north polar ice cap on Mars. It is the most detailed look to date at the insides of this ice cap. The colored map below the radar picture shows the topography of the corresponding Martian terrain (red and white represent higher ground, and green and yellow lower).
The radar image reveals four never-before-seen thick layers of ice and dust separated by layers of nearly pure ice. According to scientists, these thick ice-free layers represent approximately one-million-year-long cycles of climate change on Mars caused by variations in the planet's tilted axis and its eccentric orbit around the sun. Adding up the entire stack of ice gives an estimated age for the north polar ice cap of about 4 million years—a finding that agrees with previous theoretical estimates. The ice cap is about 2 kilometers (1.2 miles) thick.
The radar picture also shows that the boundary between the ice layers and the surface of Mars underneath is relatively flat (bottom white line on the right). This implies that the surface of Mars is not sagging, or bending, under the weight of the ice cap—and this, in turn, suggests that the planet's lithosphere, a combination of the crust and the strong parts of the upper mantle, is thicker than previously thought.
A thicker lithosphere on Mars means that temperatures increase more gradually with depth toward the interior. Temperatures warm enough for water to be liquid are therefore deeper than previously thought. Likewise, if liquid water does exist in aquifers below the surface of Mars, and if there are any organisms living in that water, they would have to be located deeper in the planet.
The topography data are from Mars Orbiter Laser Altimeter, which was flown on NASA's Mars Global Surveyor mission.
NPLD stands for the north polar layered deposits.
BU stands for basal unit, an ice-sand deposit that lies beneath parts of the north polar layered deposits.
The Shallow Radar instrument was provided by the Italian Space Agency. Its operations are led by the University of Rome and its data are analyzed by a joint U.S.-Italian science team. JPL, a division of the California Institute of Technology, Pasadena, manages the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter for the NASA Science Mission Directorate, Washington.

 Planetary Data System
Planetary Data System